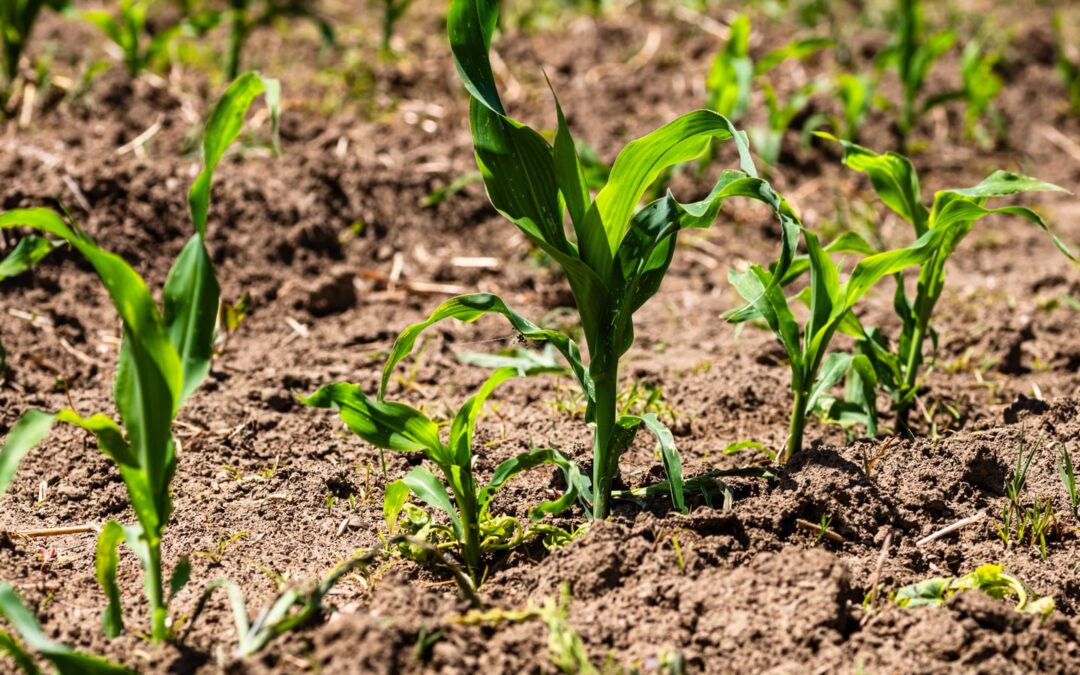



The Unexpected Protein Connection in Maize Growth and Defense
Maize (corn) is one of the most important staple crops in the world and has been extensively studied. Yet, many aspects of the genetic mechanisms regulating its growth and development remain unexplored. Recent research revealed that a family of proteins called COI1,...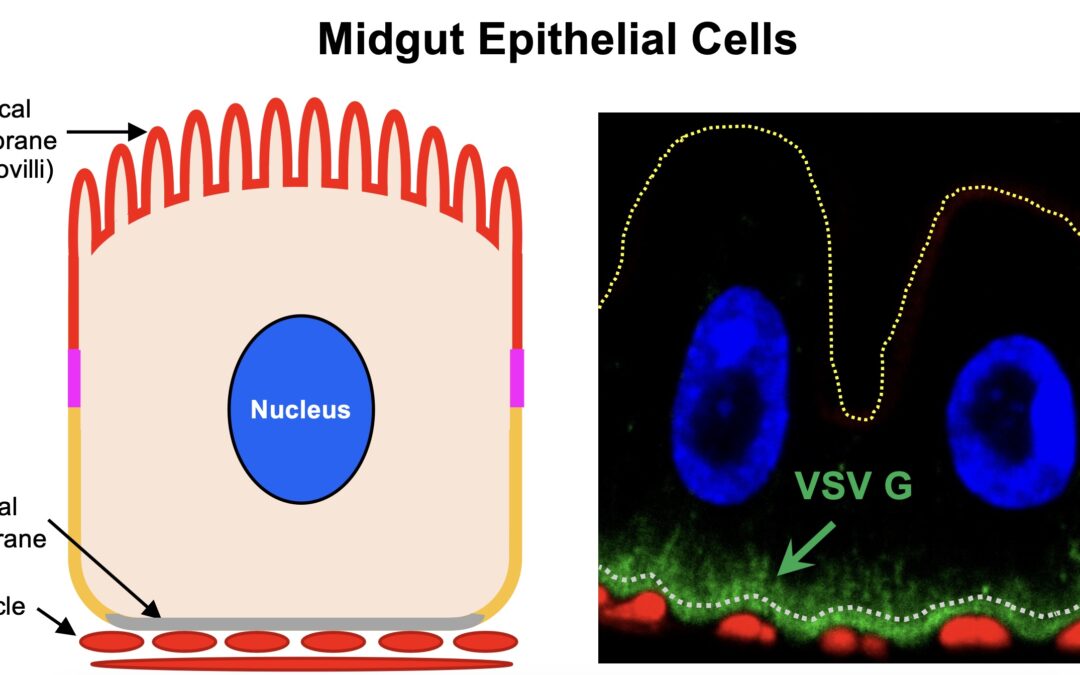
How Viruses Move Through Insects for Transmission of Diseases
Viruses are master parasites that have adapted to infect many host species. Some viruses even use multiple hosts to spread their infections – such as arboviruses that use insects to move their infections to mammalian hosts like humans. Understanding how they move...
Faculty Cluster Hire: Promoting Collaboration and Addressing Gender Bias in Academic Hiring
In the world of academic science, hiring new faculty members typically follows a predictable pattern: candidates apply individually and are evaluated primarily on their personal achievements. What if there was a way to build more collaborative, diverse teams of...
Unlocking the Secrets of Salt Stress Tolerance in Wild Tomatoes
As our climate changes and soil salinity increases in many agricultural areas, finding crops that can thrive in these challenging conditions is crucial. Cultivated tomatoes, while delicious, often struggle in salty soils. Their wild cousins, however, have evolved to...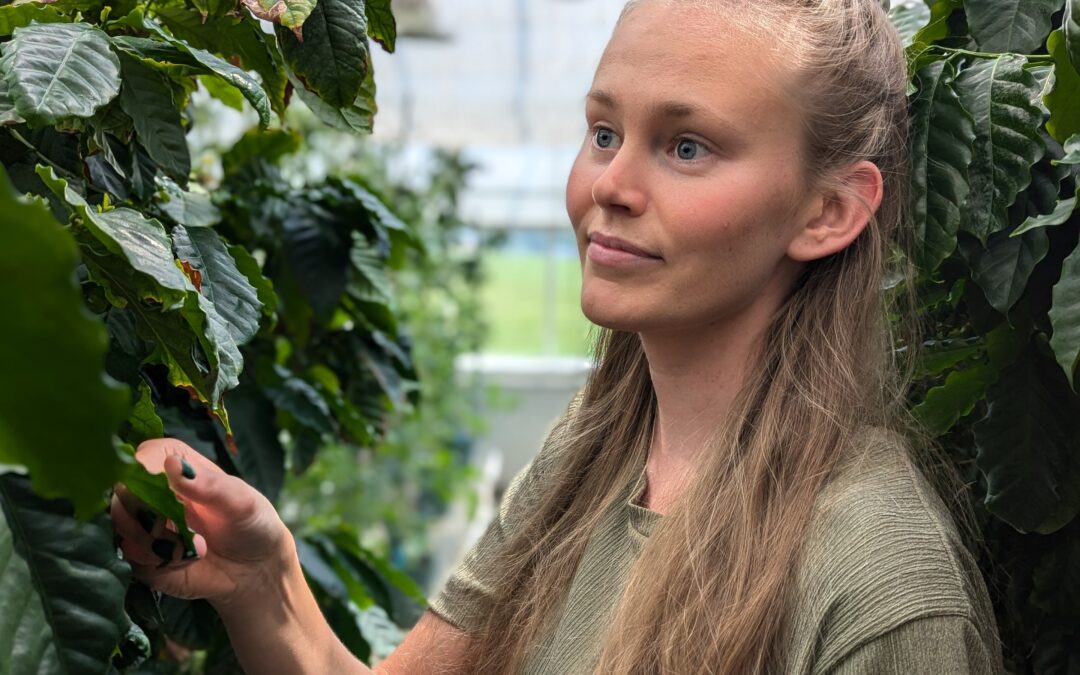
The surprising connection between your morning coffee and the battle between plants and herbivory insects
Written by: Matilda Bergsten, Jander Lab REU ResearcherEvery day, millions of cups of coffee are consumed all around the world. It is a beverage that is an integral part of the daily routines of many different cultures.Coffee isn’t just popular for its taste. Almost...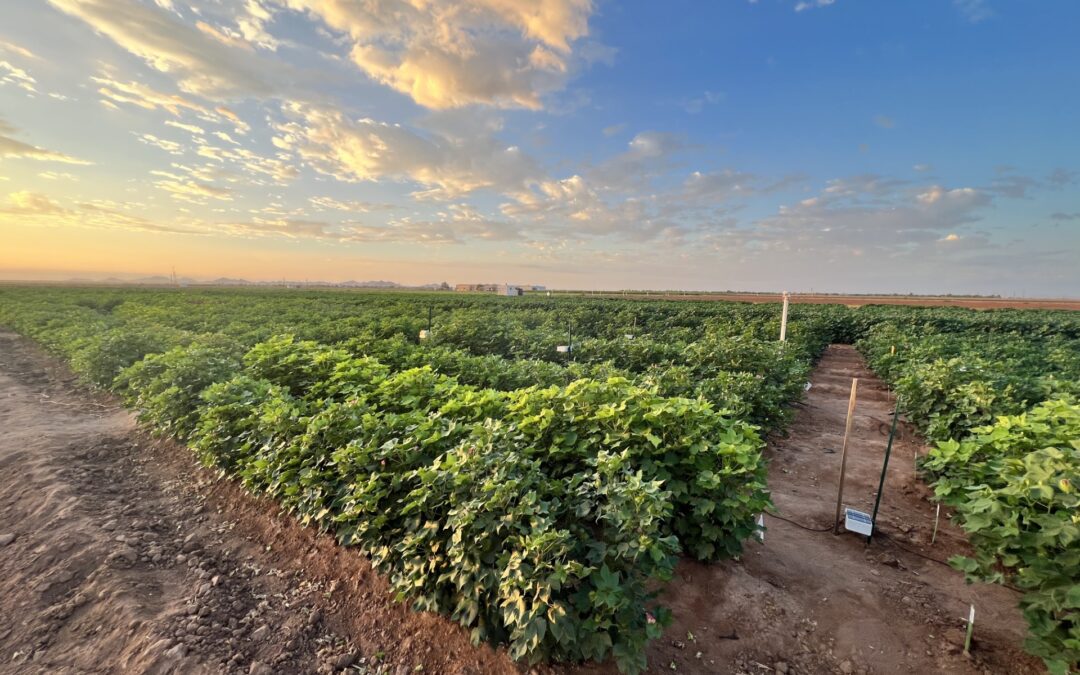
From Genes to Jeans: New Genetic Insights May Lead to Drought Resilient Cotton
Cotton is woven into the very fabric of our lives, from soft T-shirts to comfortable jeans and cozy bedsheets. It’s the world’s leading renewable textile fiber and the backbone of a global industry worth billions.As climate change intensifies, cotton farmers face...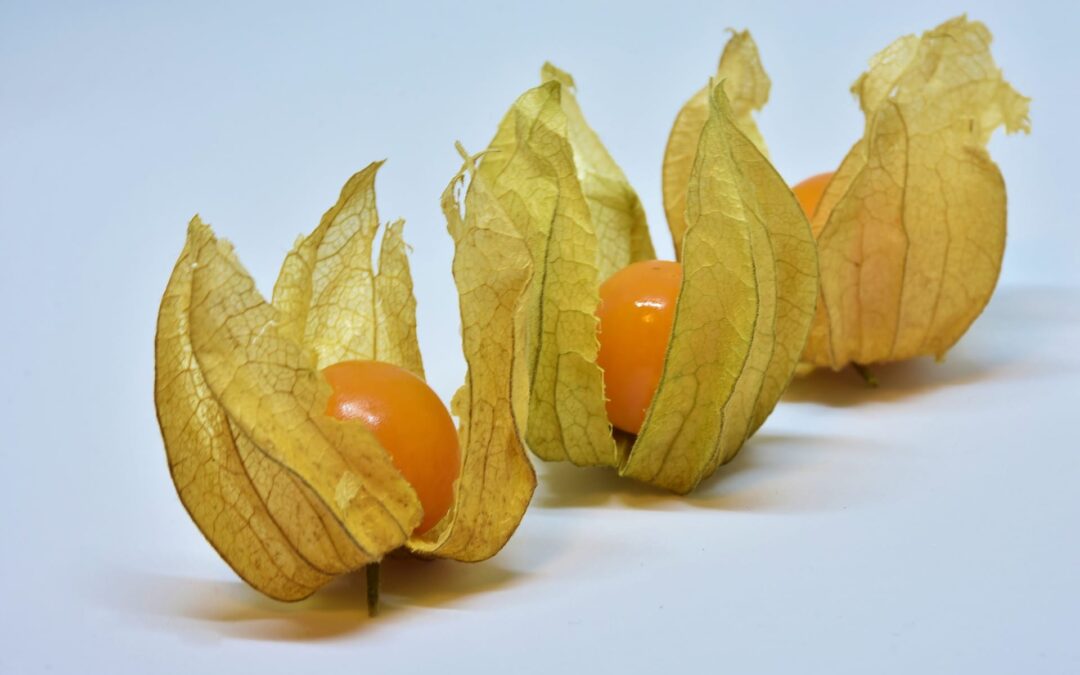
Groundcherry Gets Genetic Upgrades: Turning a Garden Curiosity into an Agricultural Powerhouse
Imagine a small fruit that tastes like a cross between a tomato and a pineapple, wrapped in its own natural paper lantern. That’s the groundcherry (Physalis grisea) – a little-known relative of tomatoes that’s been quietly growing in gardens and...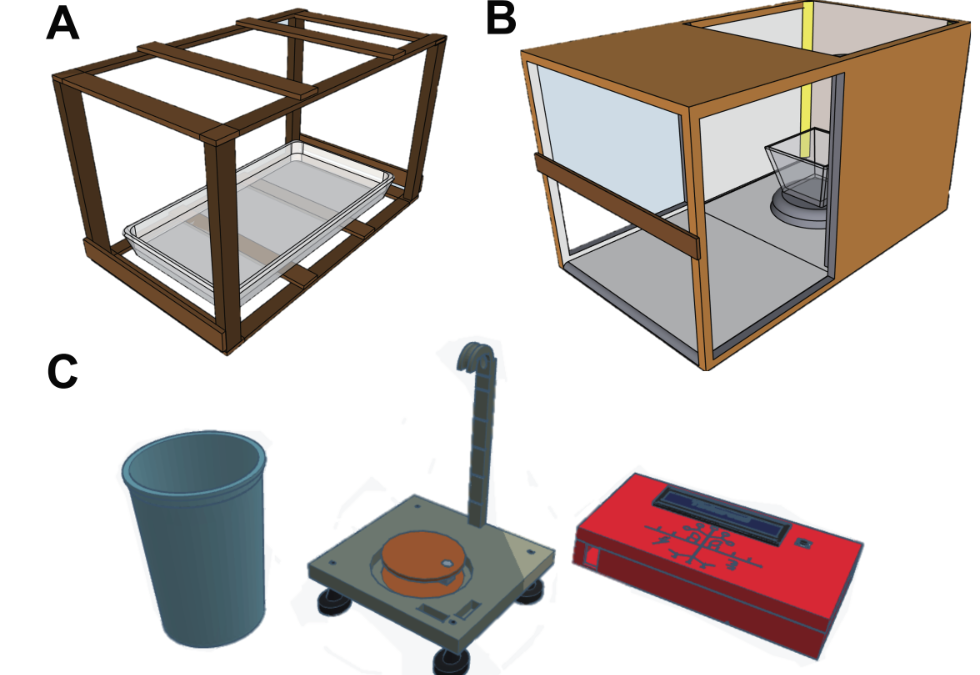
Democratizing Plant Research: A New Cost-Effective Solution for Advanced Phenotyping
Phenotyping, which involves assessing observable plant characteristics, is crucial for understanding plant development and response to environmental stresses. Traditional methods are often cumbersome, costly, and destructive, limiting research scope and scale. A new...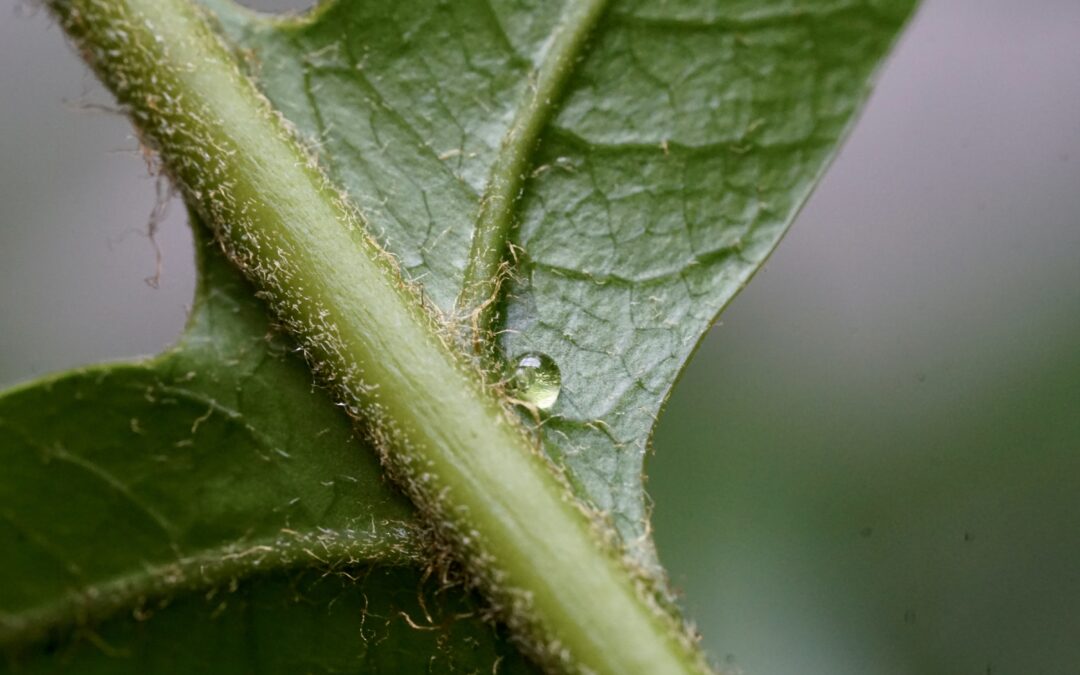
Tracing the Evolution of Ferns’ Surprisingly Sweet Defense Strategy
Plants and the animals that eat them have evolved together in fascinating ways, creating a dynamic interplay of survival strategies. Many plants have developed physical and chemical defenses to fend off herbivores. A well-known strategy in flowering plants is to...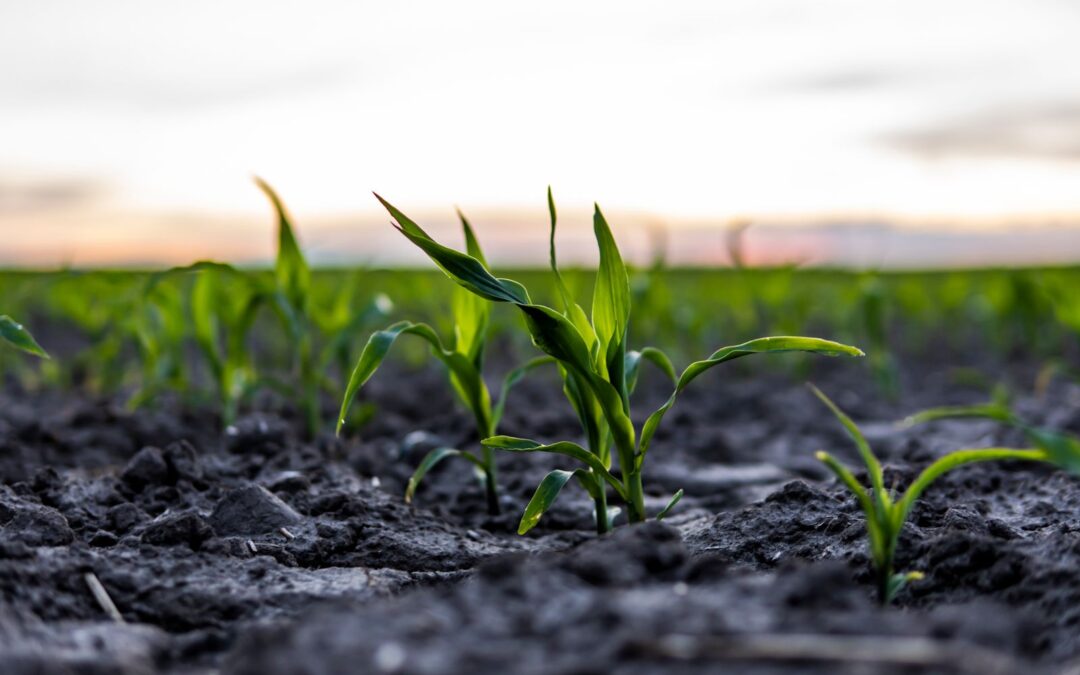
Transgenic Expression of Rubisco Factors Increases Photosynthesis and Chilling Tolerance in Maize
Maize is one of the world’s most widely grown crops and is essential to global food security. But like other plants, its growth and productivity can be limited by the slow activity of Rubisco, the enzyme responsible for carbon assimilation during photosynthesis. In a...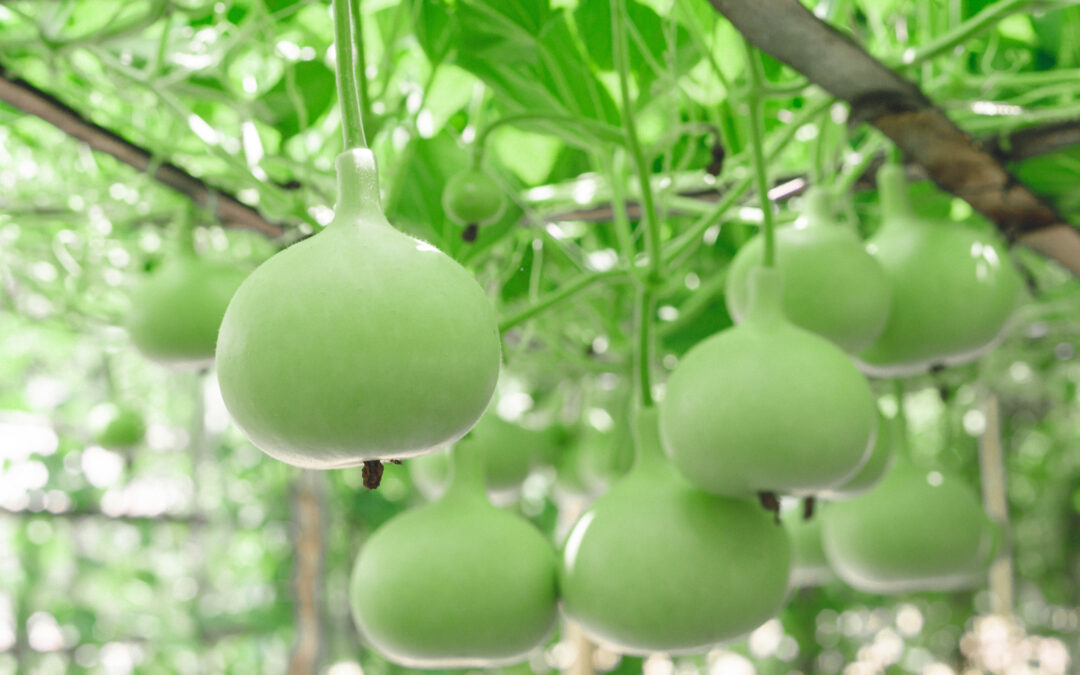
Across Oceans and Millennia: Decoding the Origin and History of the Bottle Gourd
In a fascinating dive into the past, a team of researchers from the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) and USDA has uncovered intriguing details about the origins and spread of the bottle gourd, one of the oldest domesticated crops. Their research, recently published in...
Drying Without Dying: Tracing Water Scarcity Coping Mechanisms from Mosses to Flowering Plants
Imagine: You find the dried-up remains of a once green and lush philodendron on your bookshelf and realize you can’t remember the last time you watered your houseplants. You soak the soil with water, hoping you can breathe life back into its desiccated husk, but it is...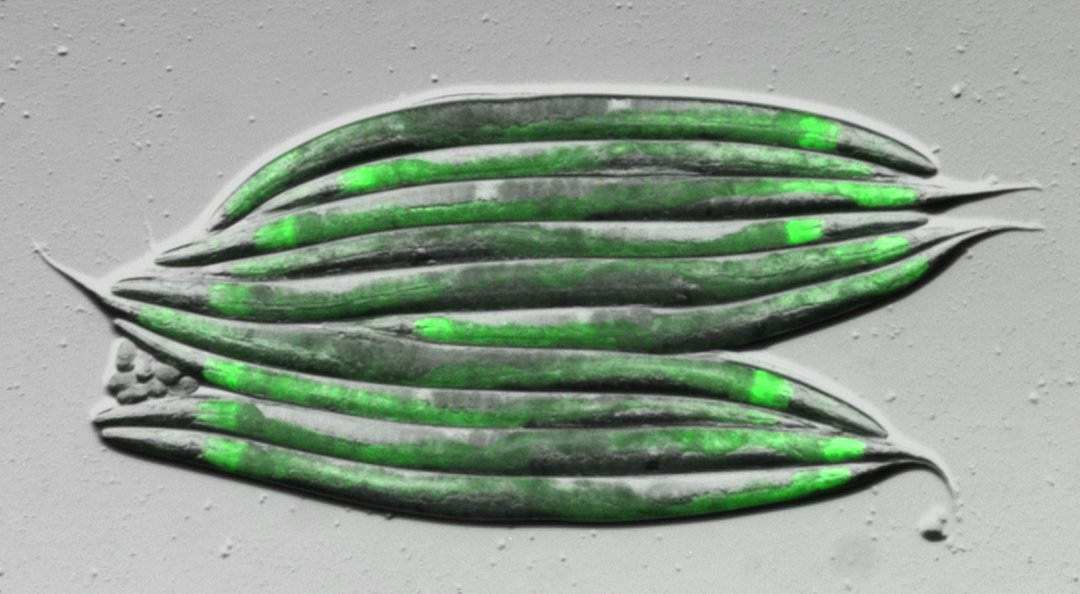
Bridging Diet, Microbes, and Metabolism: Implications for Metabolic Disorders
Mounting evidence suggests that the secret to understanding human health and combating metabolic diseases lies hidden within the microscopic world of our gut bacteria. Recent research by scientists at the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) and Cornell University reveals...
Synopsis of paper: Evolutionarily related host and microbial pathways regulate fat desaturation in C. elegans
In our paper, recently published in Nature Communications, we (my colleagues at the Boyce Thompson Institute and Cornell University) demonstrated that a specific type of bacteria-derived fatty acid – so-called cyclopropane fatty acids, which are also part of the human...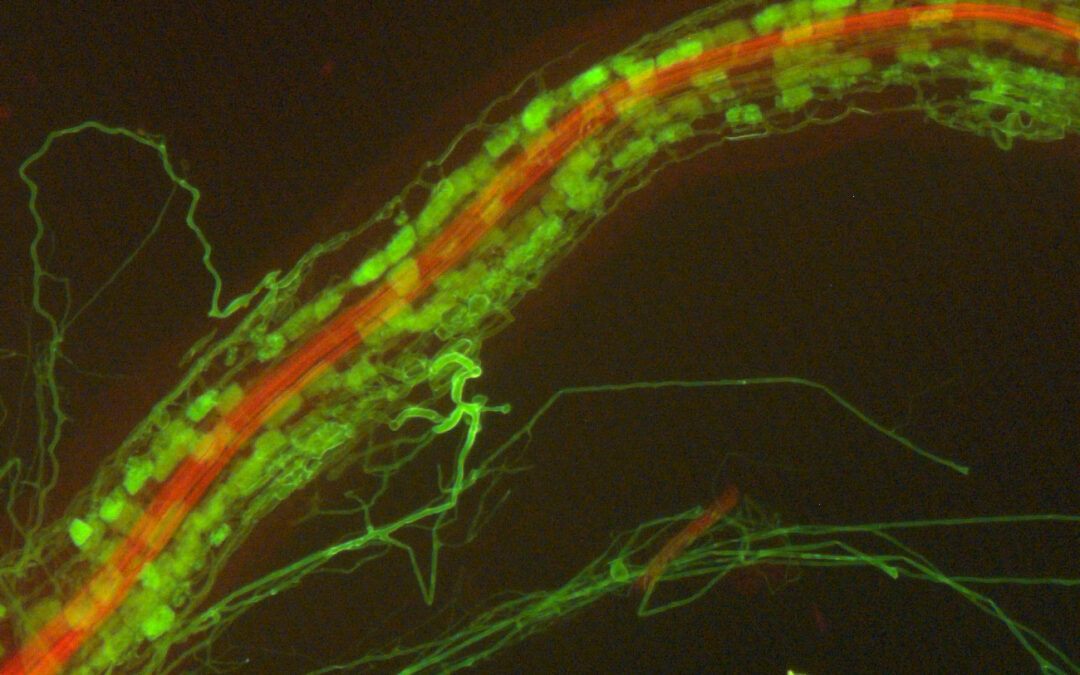
The Underground Network: Decoding the Dynamics of Plant-Fungal Symbiosis
The intricate dance of nature often unfolds in mysterious ways, hidden from the naked eye. At the heart of this enigmatic tango lies a vital partnership: the symbiosis between plants and a type of fungi known as arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi. New groundbreaking...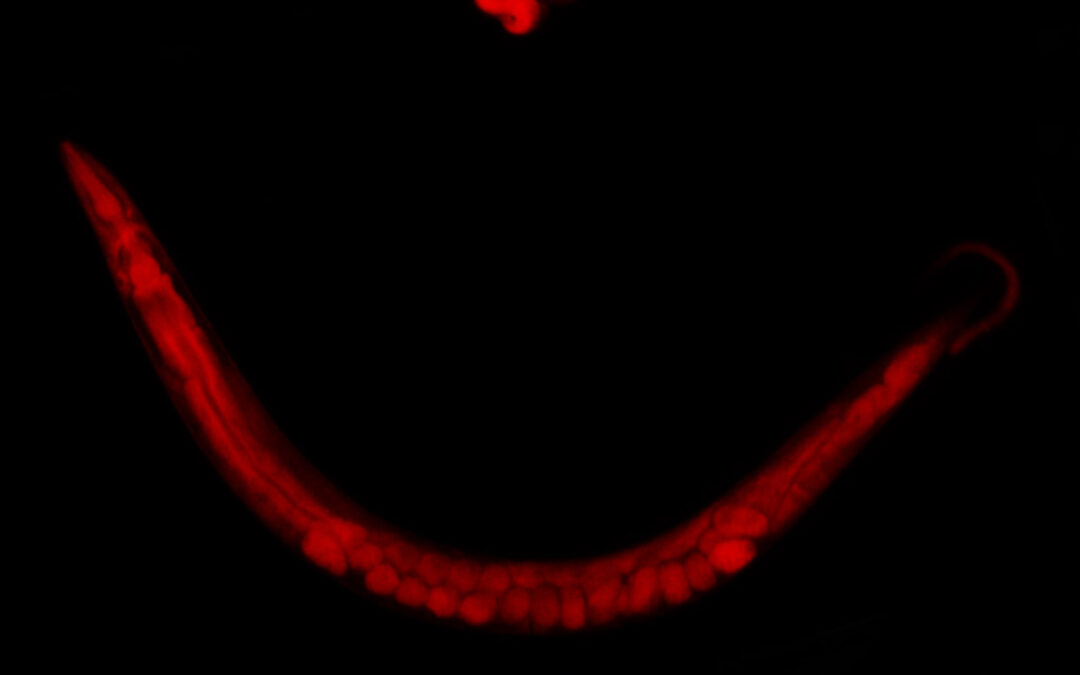
Tiny Worm, Giant Leap: Discovery of Highly Specific Fatty Acid Attachment to Proteins
In a world where the intricacies of molecular biology often seem as vast and mysterious as the cosmos, a new groundbreaking study delves into the microscopic universe of proteins, unveiling a fascinating aspect of their existence. This revelation could hold profound...
A Window into Plant Evolution: The Unusual Genetic Journey of Lycophytes
An international team of researchers has uncovered a remarkable genetic phenomenon in lycophytes, which are similar to ferns and among the oldest land plants. Their study, recently published in the journal PNAS, reveals that these plants have maintained a consistent...
Plant Warfare: The Crucial Function of Nrc Proteins in Tomato Defense Mechanisms
In the fascinating world of plant biology, an innovative study recently featured on the cover of The Plant Journal has been turning heads. The research delves into the intricate defense mechanisms of tomatoes against the notorious bacterial pathogen, Pseudomonas...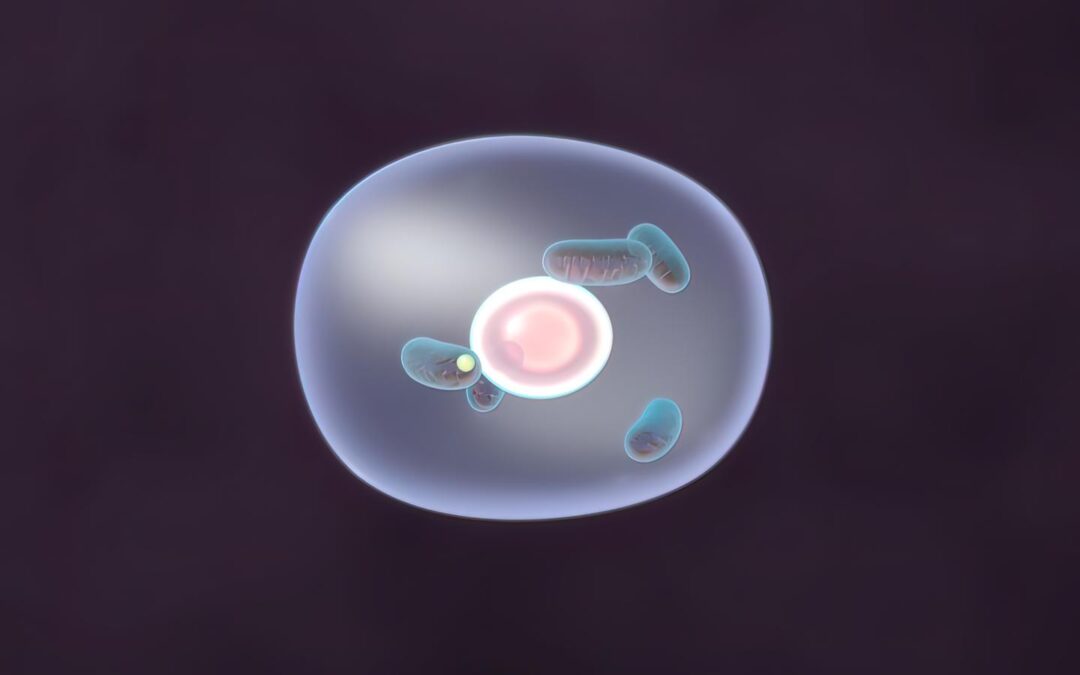
Deciphering Molecular Mysteries: New Insights into Metabolites That Control Aging and Disease
In a significant advancement in the field of biochemistry, scientists at BTI and Cornell University have uncovered new insights into a family of metabolites, acylspermidines, that could change how we understand aging and fight diseases.The study, recently published in...
2023 PGS Triad Mini-grant Awardees
We are excited to announce the recipients of the 2023 Triad funded PGS Mini-grant Program. Congratulations to all the awardees and thanks to all the participants! The committee of PGS members along with a faculty advisor reviewed a total of 8 proposals and have...
BTI Researchers Unlocking Hornworts’ Secrets
Hornworts are a little-studied, ancient group of plants with some very unique biology, including their methods of securing carbon and nitrogen. Unlocking these secrets may help researchers boost agricultural output and use less synthetic fertilizer, as well as provide...
Plant Gene Discovery Could Help Reduce Fertilizer Pollution in Waterways
Over-fertilization of agricultural fields is a huge environmental problem. Excess phosphorus from fertilized cropland frequently finds its way into nearby rivers and lakes. A resulting boom of aquatic plant growth can cause oxygen levels in the water to plunge,...
BTI Researchers Discover Compound that Speeds Sexual Development and Decline
Every day, people are exposed to myriad chemicals, both natural and synthetic. Some of these compounds may affect human physical development, but testing them directly on people would be grossly unethical. To get around this dilemma, researchers from Boyce Thompson...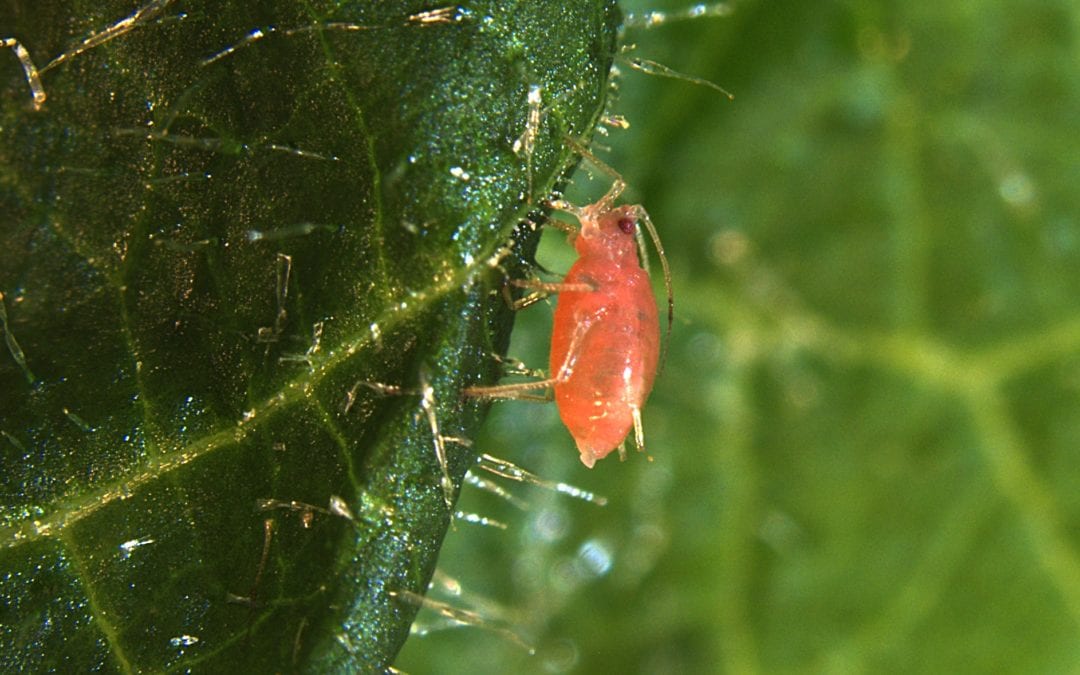
BTI Researchers Discover Interactions Between Plant and Insect-Infecting Viruses
Aphids and the plant viruses they transmit cause billions of dollars in crop damage around the world every year. Researchers in Michelle Heck’s lab at the USDA Agricultural Research Service and Boyce Thompson Institute are examining the relationship at the molecular...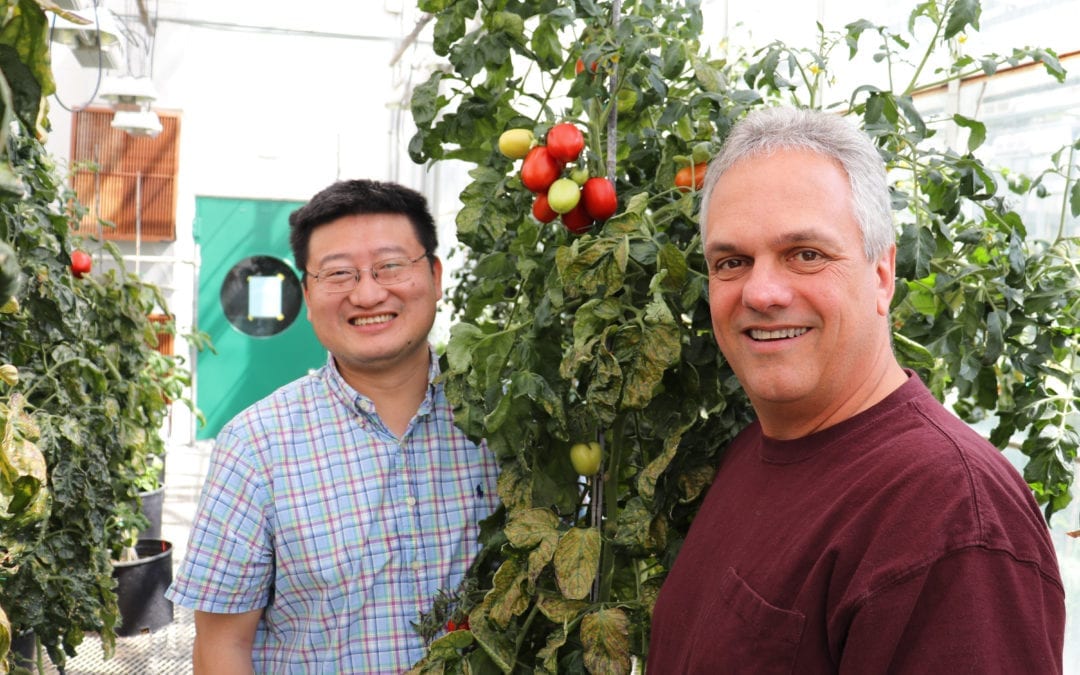
BTI Scientists Create New Genomic Resource for Improving Tomatoes
Tomato breeders have traditionally emphasized traits that improve production, like larger fruits and more fruits per plant. As a result, some traits that improved other important qualities, such as flavor and disease resistance, were lost. Researchers from Boyce...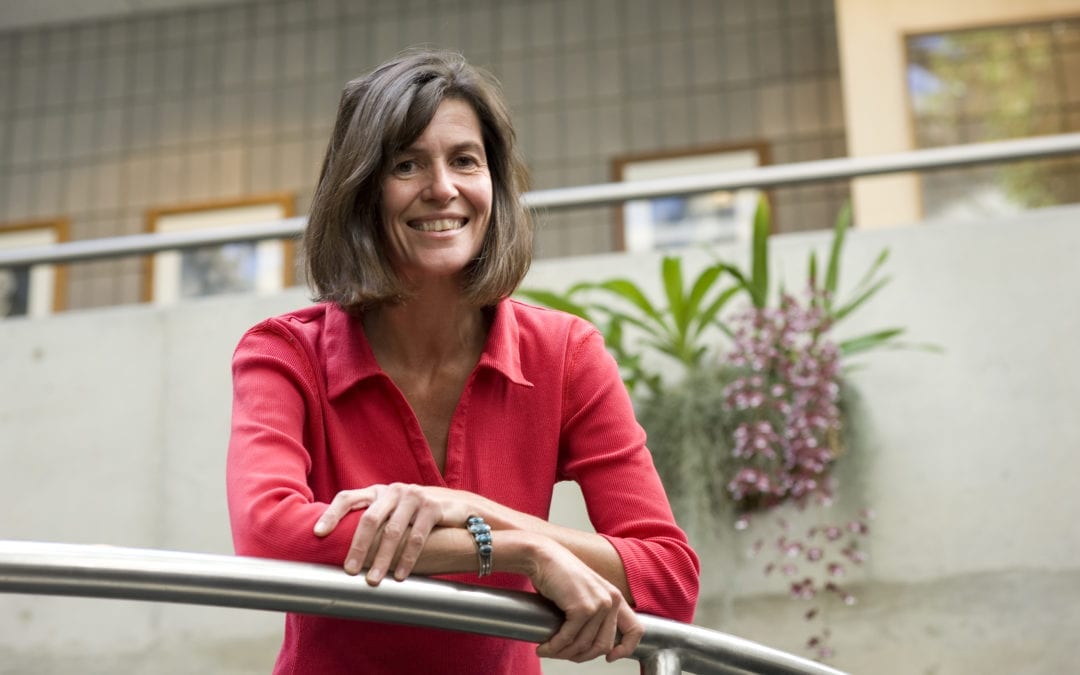
BTI’s Maria Harrison Elected to National Academy of Sciences
Maria Harrison, William H. Crocker Professor at Boyce Thompson Institute and Adjunct Professor in the School of Integrative Plant Science (SIPS) at Cornell University, has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences. Harrison is one of 100 new members announced...
BTI’s Big Red Anniversary: 40 Years at Cornell
The Boyce Thompson Institute of Corvallis, Oregon? It almost happened. April 24 will mark the 40th anniversary of the dedication ceremony for BTI’s current facilities on the Cornell University campus in Ithaca, NY. The Institute’s researchers and staff will celebrate...
BTI Promotes Faculty Member Fei
David Stern, president of the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI), is delighted to announce that faculty member Zhangjun Fei has been promoted to Full Professor on February 27, 2019. Fei was evaluated on his achievements to date and the potential he possesses. Fei has made...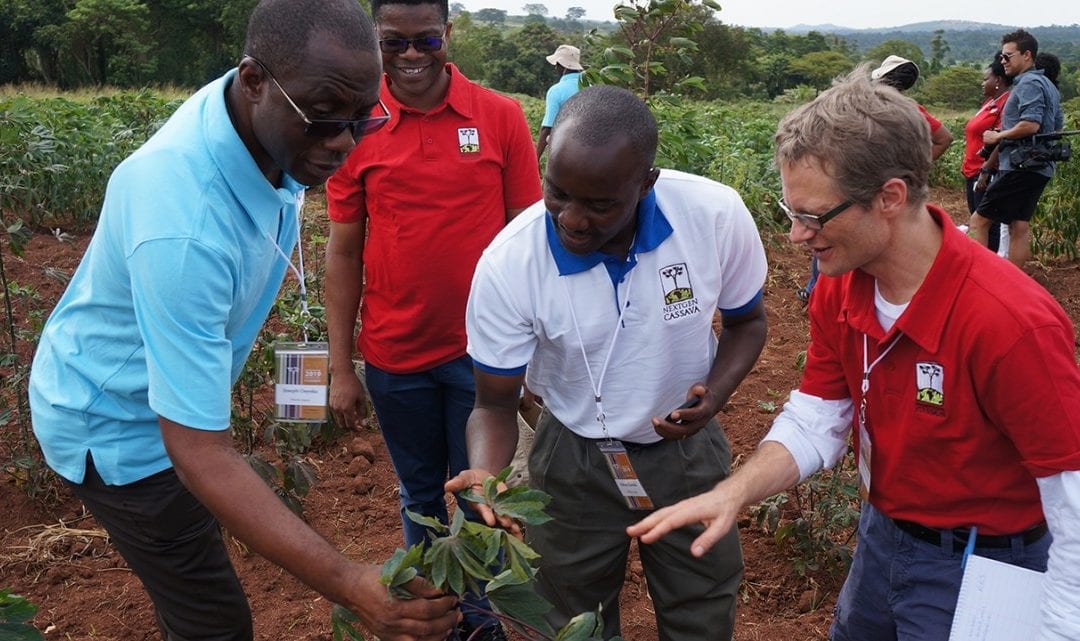
Cassava experts gather to champion ‘orphan crop’
It’s a dietary staple for millions of Africans, but cassava has traditionally received little attention from scientists and plant breeders in comparison to cash crops such as wheat and maize. However, researchers have recently been working to find cassava a scientific...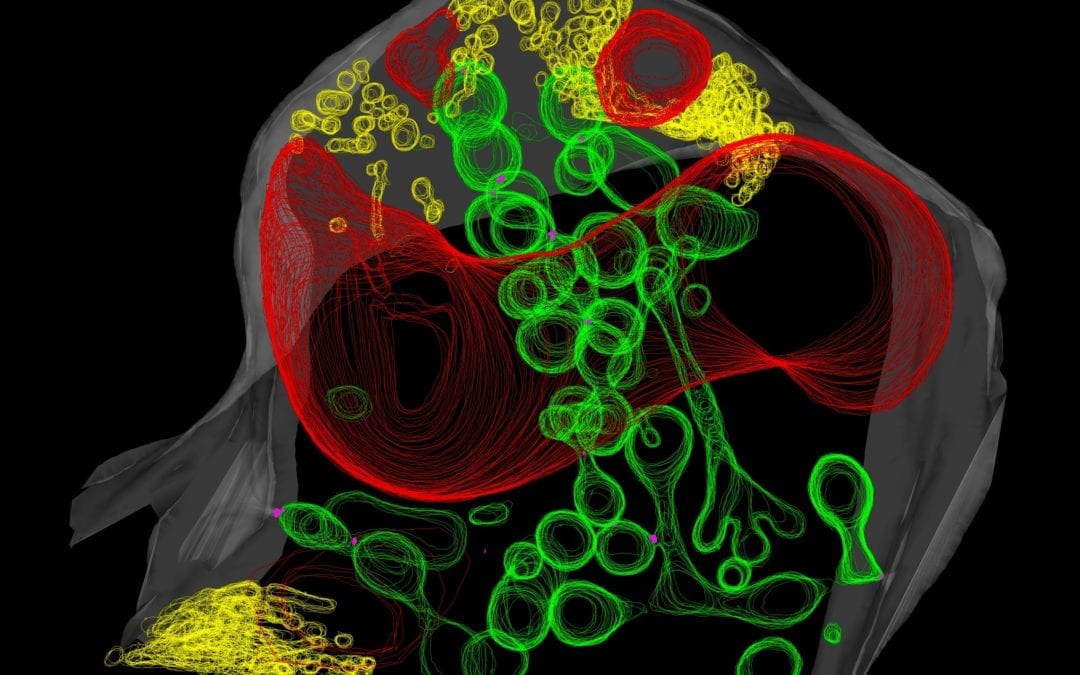
Plant–Fungal Interface Gets Tubular
For hundreds of millions of years, plants and fungi have formed symbiotic relationships to trade crucial nutrients, such as phosphate and fatty acids. This relationship is extremely important to the growth and survival of both organisms, and solving the mystery of how...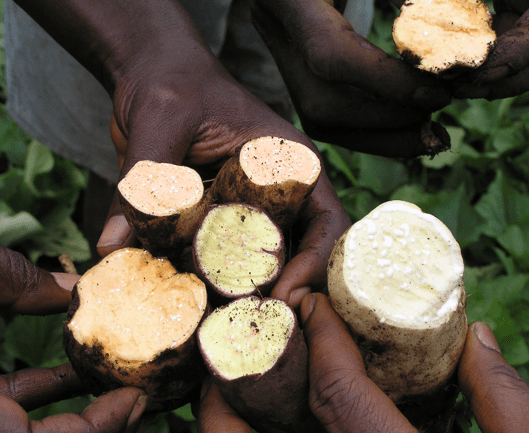
Orange is the new white: New sweetpotato data is something to be thankful for
The genome sequences of I. trifida and I. triloba can be used as robust references to facilitate sweetpotato breeding. The genomic resources developed in this study set the stage for increased rates of genetic gains for key traits such as yield, resistance to disease, and high beta-carotene.
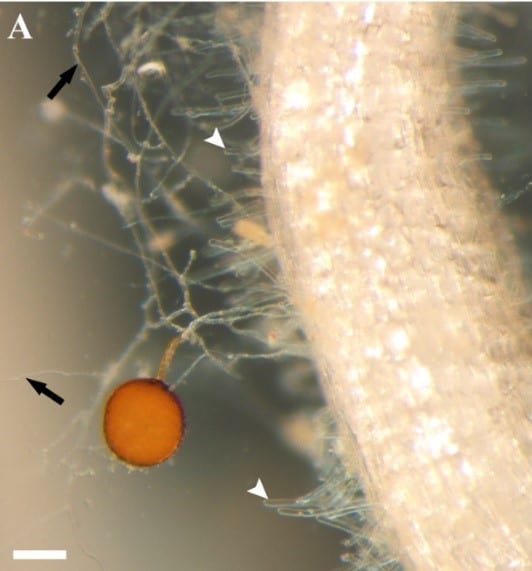
Back to our roots: Insights from genomes of a plant-associated fungus and its bacterial endosymbionts
In an article published this month in the journal New Phytologist, researchers at the Boyce Thompson Institute and the National Center for Genome Resources describe the genome sequences (DNA sequences), of the fungus Diversispora epigaea (formerly known as Glomus...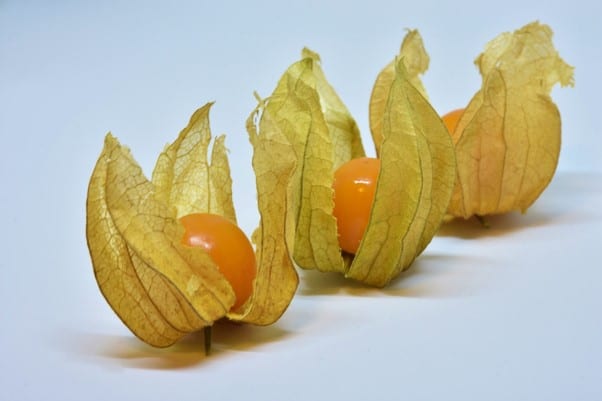
CRISPR tames the wild groundcherry
ITHACA, NY – You might not have heard of the groundcherry, or at least, never tasted one. But that could soon change thanks to research from the Van Eck Laboratory at Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI). The groundcherry (Physalis pruinosa) is approximately the same size...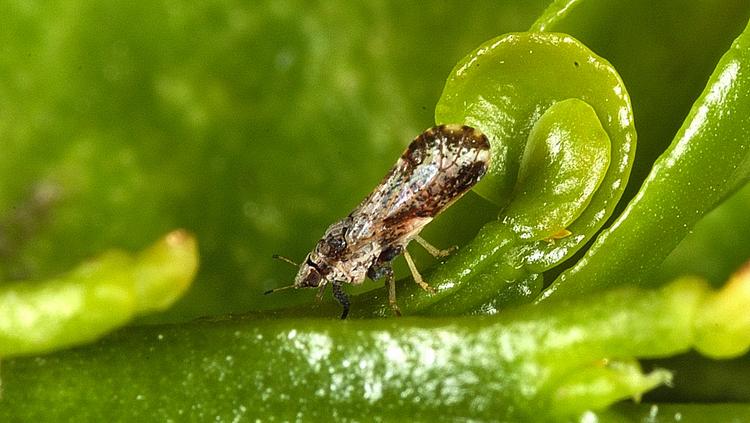
Blood, sweat and tears: All in a day’s work fighting citrus greening disease
Around this time last year, PhD student Angela Kruse and postdoctoral scientist Dr. John Ramsey were huddled over microscopes, using tiny needles to painstakingly extract blood, also known as hemolymph, from 300 Asian citrus psyllids – insects about the size of...
NSF awards BTI $1M to study plant-bacteria symbiosis
Professor Dr. Fay-Wei Li has been awarded a $1.1 million NSF grant to study hornwort/bacteria symbiosis. The hornwort plant relies on nitrogen-fixing soil bacteria to give it life and unlocking the secrets to how that works may help reduce agricultural dependence on...
Open-access wild tomato genome offers valuable insights for tomato growers, crop scientists
The new S. lycopersicoides genome sequence offers the opportunity for innovative breeding programs that may hold the ability to confer desirable traits to marketable tomato varieties.
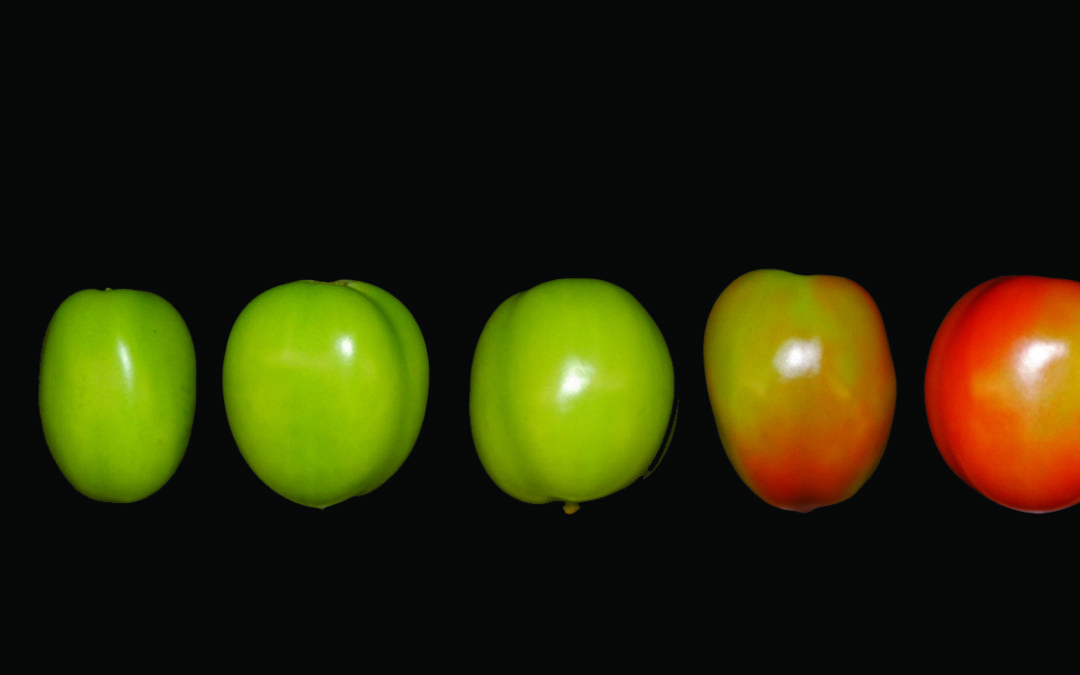

New ‘Tomato Expression Atlas’ dives deep into the fruit’s flesh
Researchers at BTI, Cornell and USDA published a spatiotemporal map of gene expression across all tissues and developmental stages of the tomato fruit – the genetic information underlying how a fruit changes from inside to out as it ripens. Their data is available in the new Tomato Expression Atlas (TEA).

Maria Harrison, consortium of scientists receive $5 million grant to study genes that help legumes access soil nutrients
BTI’s Harrison lab will develop Medicago truncatula mutants to identify the function of genes predicted to be important in nitrogen fixation in legumes.
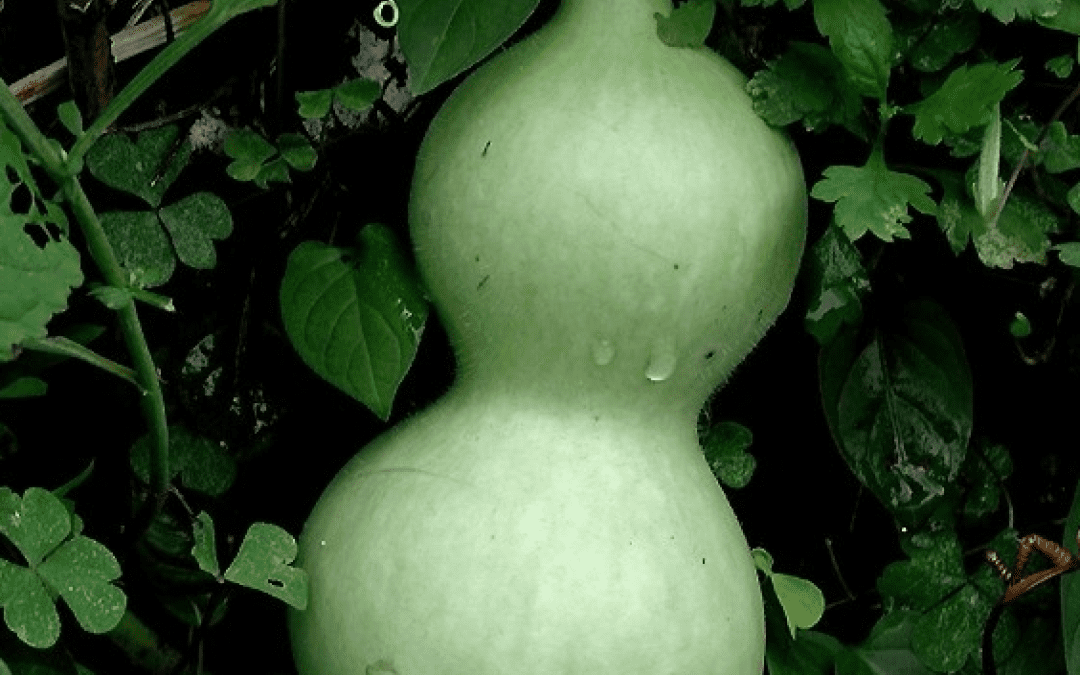

Bottle gourd genome provides insight on evolutionary history and genetic relationships of cucurbit crops
In their findings, researchers compared the sequenced bottle gourd genome to those of other cucurbit species, allowing them to reconstruct the ancient genomic history of the Cucurbitaceae family.
Pumpkin genomes sequenced revealing uncommon evolutionary history
For some, pumpkins conjure carved Halloween decorations, but for many people around the world, these gourds provide nutrition. Scientists at Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) and the National Engineering Research Center for Vegetables in Beijing have sequenced the genomes of two important pumpkin species, Cucurbita maxima and Cucurbita moschata.
$9.4M NIH grant funds chronic fatigue syndrome center
Cornell will receive close to $9.4 million over five years to establish the Cornell Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Collaborative Research Center, which will span Cornell’s Ithaca campus, Weill Cornell Medicine, Ithaca College, the Boyce Thompson Institute [Schroeder Lab], the Workwell Foundation, EVMED Research, the SOLVE ME/CFS Initiative and private ME/CFS medical practices.
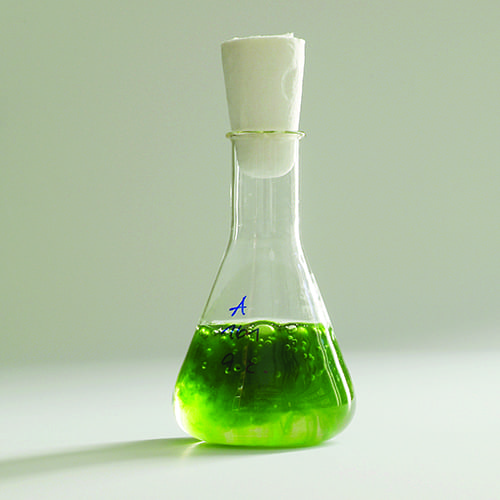

Bioreactors on a chip renew promises for algal biofuels
This week, researchers from Boyce Thompson Institute and Texas A&M University report in Plant Direct exciting new technology that may revolutionize the search for the perfect algal strain: Algal droplet bioreactors on a chip.

International team collaborates to decipher the Asian citrus psyllid genome
BTI’s Mueller and Heck Labs, in collaboration with 21 partner institutions, recently published a draft assembly and annotation of the D. citri genome.

Hot tomatoes! MPMI Cover features BTI research
This month, the cover of Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions features a publication by Simon Schwizer from the Martin Lab at BTI that furthers our understanding of how tomatoes are able to resist infection by Pseudomonas syringae, the causal agent of bacterial speck, a common disease in upstate NY.

GOBii initiative bridges plant breeding digital divide
With open-source software, GOBII plans to provide organizations in the developing world with the computational infrastructure needed for efficient breeding.
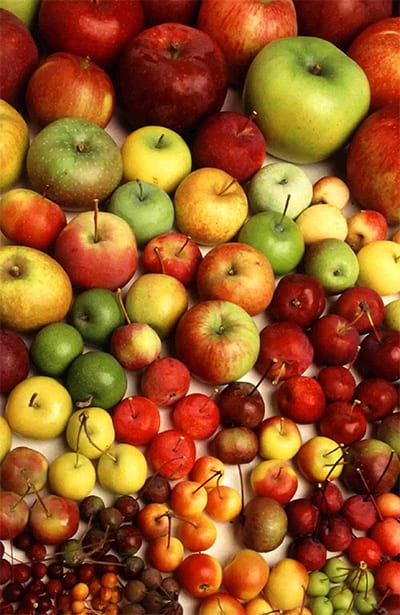

New genomic insights reveal a surprising two-way journey for apple on the Silk Road
New research out of Boyce Thompson Institute reveals surprising insights into the genetic exchange along the Silk Road that brought us the modern apple.
Science In Real Life: GMOs with the Van Eck Lab
Follow Science In Real Life (IRL) as they head to the Van Eck Lab and demystify GMOs by showing how they’re made in the lab.

BTI Receives DARPA “Insect Allies” Award to Develop Viruses and Insects for Maize Improvement
The research project, titled Viruses and Insects as Plant Enhancement Resources (VIPER), is supported by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Insect Allies program.
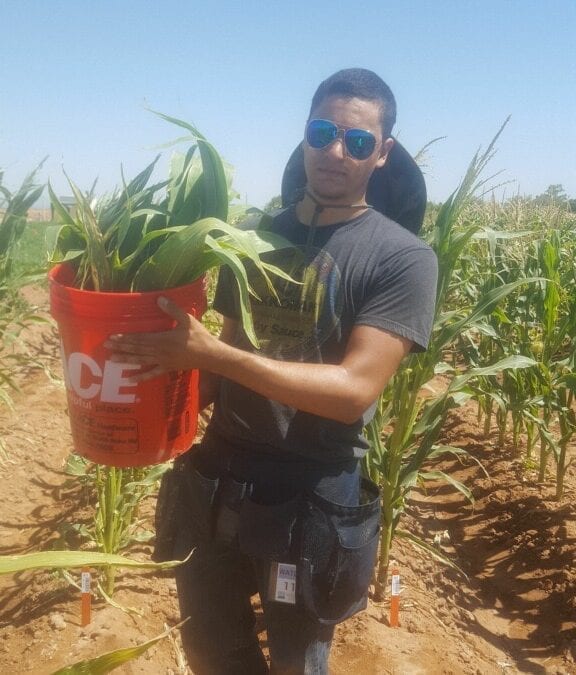

Maize in Maricopa: An Interview with Intern Michael Miller
Michael Miller spent his first two weeks as a PGRP intern at the United States Department of Agriculture’s Arid Land Research Center.
