High School Research Internship Projects
BTI’s High School Research Program provides students with 6-7 weeks of hands-on research training with existing research projects happening within plant science. Scientists work in different lab environments at BTI. Some labs are involved primarily in bioinformatics, while other labs operate in a wet lab or conduct field work. Read below for descriptions of bioinformatics and wet lab and field work. In general, most of our research projects are grouped into ones that involve a strong understanding and willingness to work with computers, and projects that involve laboratory or field work.
Bioinformatics involves work related to creating programming and software to understand and manage the large data sets that result from the research. This could involve creating programming, coding, and creating software that scientists will use. These are important and valuable skills to scientists since research often results in a lot of data—and a need to understand it! While a foundation of computer science skills (i.e. programming or coding) is important to bioinformatics projects, you can learn skills during your research project! A willingness to learn is key. Previous high school bioinformatics projects have involved using and helping create software to analyze data sets containing traits of wild watermelons to understand genes that might be important to plant breeders.
Wet Lab and field work involves working within a lab and/or in a field or greenhouse to conduct experiments and collect data. This could involve using techniques like DNA isolation and extraction and gel electrophoresis. Field work could involve planting and caring for the plants, as well as accurately collecting data for analysis. This work involves learning important skills to conduct experiments across many disciplines. Previous high school wet lab projects have involved looking at the impacts of salt stress on plants and finding genes within plants that can better handle salt stress in the environment. Previous high school field work projects have involved accurately documenting the number of bees visiting certain flowers in a greenhouse environment to understand if there are certain plant traits they like more.
Note: Some research could be mostly in a wet lab, and some mostly in a field, or a mix of both. Often times a project won’t involve field work. Below you will see labs labeled as ‘Wet lab and field work’, but not all will involve field work.
The following list reflects typical research programs and projects where students may be placed. Read through this list to help you better understand the types of lab placements and determine which type of lab experience you are interested in. We ask all high school students who are applying through our application form to select the type of lab experience they are interested in, not which lab they want to be placed in. However, if one of these projects seems very interesting to you, you may indicate that within your essay.
To learn more about potential projects and their faculty sponsors, click on the topics below.
Bioinformatics and genomics to understand important traits of agricultural crops - Fei Lab, BTI
Bioinformatics Lab
Using integrated bioinformatics and genomics approaches to understand important traits of agricultural crops.
Project description:
 The development of high throughput technologies has given rise to a wealth of information at system level including genome, transcriptome, proteome and metabolome. However, it remains a major challenge to digest the massive amounts of information and use it in an intelligent and comprehensive manner. To address this question, Dr. Fei’s group has focused on developing computational tools and resources to analyze and integrate large scale “omics” datasets”, which help researchers to understand how genes work together to comprise functioning cells and organisms.
The development of high throughput technologies has given rise to a wealth of information at system level including genome, transcriptome, proteome and metabolome. However, it remains a major challenge to digest the massive amounts of information and use it in an intelligent and comprehensive manner. To address this question, Dr. Fei’s group has focused on developing computational tools and resources to analyze and integrate large scale “omics” datasets”, which help researchers to understand how genes work together to comprise functioning cells and organisms.
Faculty advisor: Zhangjun Fei

Developing computerd vision approaches to visualize long-distance transport - Frank Lab, Cornell
Bioinformatics lab
Project description:
Xylem-mobile dye moving through a pepper leaf (image credit: Hannah Thomas)
Long-distance signals are transported between grafted root and shoot systems through the plant vascular network. Summer students will combine genetic engineering, fluorescence imaging, and computer vision based approaches to automate the detection of vascular tissue and track long-distance transport of mobile dyes and proteins through the plant vascular system. This work will require some computational background as well as interest in plant physiology and microscopy.
Faculty advisor: Margaret Frank

Molecular and genetic analysis of fruit ripening and related nutrient pathways, using tomato as the model system - Giovannoni Lab, BTI
Wet lab and field work
Project description:

Ripening is a process by which the texture, color, flavor, and nutritional content of fruit is enhanced. These traits contribute to the healthfulness and desirability of the fruit as a food source. Clearly, understanding the processes behind fruit ripening are important in terms of nutrition, but also for commercial applications such as transportation and shelf-life. Thus, the focus of research in the Giovannoni lab is molecular and genetic analysis of fruit ripening, related signal transduction systems and pathways leading to accumulation of nutritional compounds, using tomato as a model system. Researchers in the lab have characterized numerous genes related to ripening control and manifestation. In addition to identifying important genomic and regulatory components of ripening, the lab also investigates regulation of lycopene synthesis and accumulation in fruit. Lycopene is the pigment that gives tomatoes their red coloring and which is also suggested to inhibit degenerative diseases such as cancer and heart disease. Using a genomics approach, the lab is investigating the regulatory mechanisms behind accumulation of this important compound.
For more information about the Giovannoni lab, please visit the Plant Biology website. Additionally, the Giovannoni lab, in conjunction with other labs on campus has developed a resource for tomato genomics, the Tomato EST Database. Additional resources and information resulting from tomato genomics activities on the Cornell campus can be found at the Solanaceae Genomics Network site.
Faculty advisor: Jim Giovannoni

Molecular genetic studies of temperature responses and immune responses in plants - Hua Lab, Cornell
Project description:

Proper responses to environmental signals are essential for plant growth, reproduction, and fitness. Understanding the molecular genetic basis of such responses is not only fundamental to the central biological question of signaling and adaptation, but also better prepares us for global climate changes.
Research programs in Hua lab include molecular genetic studies of 1) temperature regulation of plant growth, 2) regulation of plant immunity, and 3) interplay between temperature and immunity. Both induced mutations and natural variations of Arabidopsis and rice are used to dissect signaling pathways and reveal adaptive changes in signaling. These studies aim at a deeper understanding of how plants adapt and evolve in a changing environment.
Faculty advisor: Jian Hua

Genetic and biochemical mechanisms of plant defense against insects - Jander Lab, BTI
Wet lab and field work
Project description:
 Plants in nature are subject to attack by wide variety of caterpillars, beetles, aphids, and other insect herbivores. Although there are a million or more species of herbivorous insects, any individual plant species is resistant to the vast majority of these. Insect feeding is inhibited by an array of chemical defenses that exhibits great variability both within and among different plant species. However, although it is known that any plant leaf contains several thousand different metabolites, most of these remain unidentified. In the Jander lab we are investigating natural variation in the herbivore resistance of maize, tomato, and potato to elucidate the molecular basis of plant defense traits. Through a combination of genetic crosses, gene expression assays, metabolite profiling, and insect growth experiments, we are able to identify specific plant genes, biosynthetic pathways, and metabolites that are required to mount an effective anti-herbivore defense.
Plants in nature are subject to attack by wide variety of caterpillars, beetles, aphids, and other insect herbivores. Although there are a million or more species of herbivorous insects, any individual plant species is resistant to the vast majority of these. Insect feeding is inhibited by an array of chemical defenses that exhibits great variability both within and among different plant species. However, although it is known that any plant leaf contains several thousand different metabolites, most of these remain unidentified. In the Jander lab we are investigating natural variation in the herbivore resistance of maize, tomato, and potato to elucidate the molecular basis of plant defense traits. Through a combination of genetic crosses, gene expression assays, metabolite profiling, and insect growth experiments, we are able to identify specific plant genes, biosynthetic pathways, and metabolites that are required to mount an effective anti-herbivore defense.
Faculty advisor: Georg Jander

Understanding stress-induced changes in plant architecture for improved resilience - Julkowska Lab, BTI
Wet lab and field work
Project description:
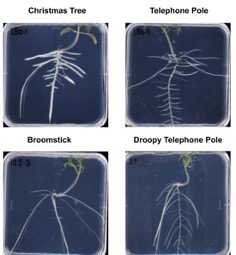
The root system architecture types that Julkowska lab has identified in wild tomato relative, S. pimpinellifollium.
Plants adjust their development to the environmental conditions. This incredible flexibility is exhibited in tropic responses, like phototropism, but also extends beyond the individual organ scale. In Jukowska lab we are interested in how environmental stress shapes plant architecture. Stress exposure often induces quiescence of growth through modification of cell cycle activity, cell expansion and cell wall extensibility. The period of initial growth arrest and the extent of recovered growth differs between individual organs leading to altered plant architecture.
Interns in Julkowska lab will explore changes to plant architecture using timeseries experiments, where the changes in plant growth are recorded using Raspberry Pi computers connected to the cameras. The images are subsequently analyzed using PlantCV software and the dynamics are examined using pipelines in R. The environmental changes are explored in domesticated plant species, such as tomato or common beans, but also across resilient species, such as Solanum pimpinellifolium, which is a close relative to cultivated tomato, but exhibits tremendous resilience to heat and drought stress, as well as cowpea, which is known for its resilience to heat and drought, and performs well in subsistence farming across the world. The data collected during the internship will form a fundaments for future genetic studies, including GWAS and RNAseq experiments, to identify the genetic components underlying changes in growth dynamics of individual organs, as well as changes in overall plant architecture. This will provide new insight into breeding targets and future strategies to ensure food security in changing climate.
Faculty advisor: Magdalena Julkowska

Seed-free plant genomics and symbioses– Li Lab, BTI
Bioinformatics lab
Project description:
 The Li lab uses genomic tools to investigate the evolution and biology of seed-free plants: ferns, fern allies, and bryophytes (mosses, liverworts, and hornworts). We are particularly interested in their symbioses with N2-fixing cyanobacteria, which provide plants with their own source of nitrogen fertilizer. We aim to understand the evolution and mechanisms of plant-cyanobacteria symbioses, and the results of which will lay the foundation for future engineering of “self-fertilizing” crops with less reliance on synthetic nitrogen fertilizers. To this end, we are surveying the diversity of cyanobacterial symbionts in hornworts, and using RNA-sequencing to uncover putative symbiosis-related genes.
The Li lab uses genomic tools to investigate the evolution and biology of seed-free plants: ferns, fern allies, and bryophytes (mosses, liverworts, and hornworts). We are particularly interested in their symbioses with N2-fixing cyanobacteria, which provide plants with their own source of nitrogen fertilizer. We aim to understand the evolution and mechanisms of plant-cyanobacteria symbioses, and the results of which will lay the foundation for future engineering of “self-fertilizing” crops with less reliance on synthetic nitrogen fertilizers. To this end, we are surveying the diversity of cyanobacterial symbionts in hornworts, and using RNA-sequencing to uncover putative symbiosis-related genes.
Faculty advisor: Fay-Wei Li

Pollinator health - pesticide, pathogen, and nutritional stress on bees - McArt Lab, Cornell

Wet lab and field work
Project description:
Why are pollinator populations declining and what can we do about it? These are core research motivations in the McArt lab. Some current projects include: 1) Understanding pathogen transmission in plant-pollinator networks. We’ve recently found that ~20% of individual flowers have bee pathogens on them (!) and are working to understand how disease spreads in bee communities via bee-flower visitation networks. 2) Investigating how fungicides impact bees during pollination of apple. We’re unraveling a complex system where interactions between fungicides, insecticides, bee microbiota, and pathogens are all at play. 3) Understanding how pollinator populations respond to mass flowering events in agricultural systems and habitat enhancements (e.g., large wildflower plantings underneath solar panels at new solar power facilities).
Approaches in our lab typically involve field and/or lab research with bees, chemical analyses (HPLC, etc.), and molecular techniques (PCR, etc.).
Bioinformatics and genomics - Mueller Lab, BTI
Bioinformatics lab
Project Description:
 Interns in the Mueller lab work on a variety of bioinformatics and genomics projects and gain experience in the following areas: genome assembly, structural and functional annotation, biochemical pathways, comparative genomics, ontology development and data presentation and visualization.
Interns in the Mueller lab work on a variety of bioinformatics and genomics projects and gain experience in the following areas: genome assembly, structural and functional annotation, biochemical pathways, comparative genomics, ontology development and data presentation and visualization.
Faculty Advisor: Lukas Mueller

Internships are funded by the National Science Foundation, Research Experiences for Undergraduates Award #1358843, individual faculty grants, and the generosity of donors including the Emerson Foundation , Ithaca Garden Club, John Ben Snow, the Legacy Foundation of Tompkins County, Rheonix, Triad Foundation Inc, Yunis Realty , and many individual donors.